Latest Update: As of the time of writing, the article published by "Health Guide" on the People's Daily's digital media platform has been removed.
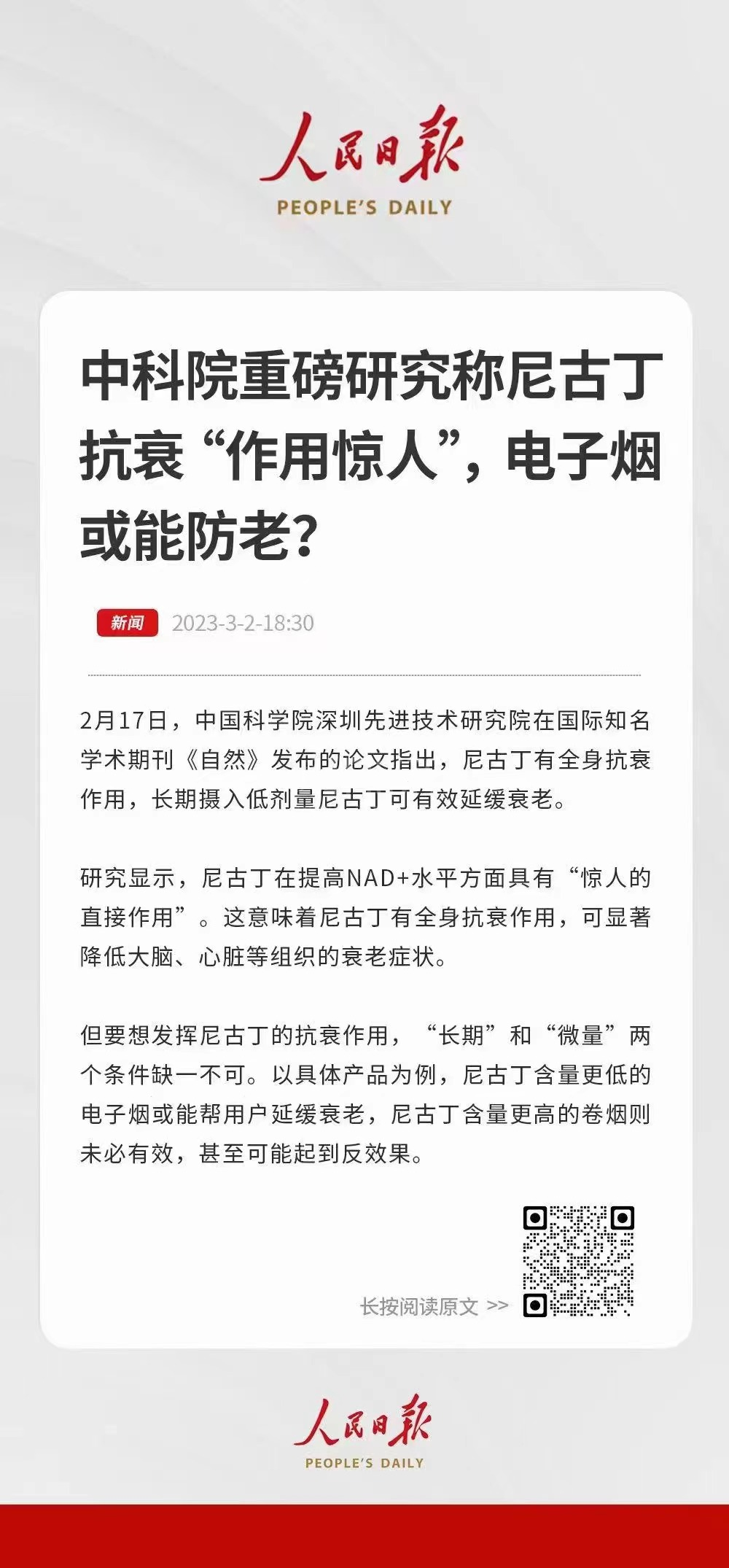
On March 2nd, an article titled "Nicotine's Amazing Anti-aging Effects: Can e-cigarettes Prevent Aging?" was published in the Health Guide section of the People's Daily's new media platform, "People's Daily Number." The article quoted from a research paper by the team led by Li Xiang from the Institute of Brain Cognition and Brain Disorders at the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The paper, titled "Nicotine rebalances NAD+ homeostasis and improves aging-related symptoms in male mice by enhancing NAMPT activity," mainly explores the impact of nicotine on the anti-aging substance NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide's oxidized form) in the human body. The paper reveals the significant effects of nicotine on NAMPT activity in mice experiments.
Health Magazine" echoes the opinion of tobacco control experts: "If you want to improve your physical health but find it difficult to quit smoking, then switch to e-cigarettes completely." The platform introduction of "Health Magazine" (also known as "Shaanxi Health Magazine") states that it is a comprehensive service newspaper approved by the National Press and Publication Administration and distributed nationwide.

Paper: Nicotine may delay age-related deterioration and cognitive decline. In a recently published study, researchers have found evidence suggesting that nicotine could potentially have a positive effect on age-related cognitive decline and deterioration. The study, conducted by a team of scientists from various institutions, aimed to explore the potential benefits of nicotine in mitigating the effects of aging on cognitive abilities. Traditionally, nicotine has been associated with harmful health effects, primarily due to its presence in tobacco products. However, emerging research has started to shed light on potential positive aspects of nicotine consumption. The study involved a sample of individuals aged 50 and above, who were divided into two groups: a control group and a nicotine group. Over a period of three years, participants in the nicotine group were administered controlled doses of nicotine, while those in the control group received a placebo. Various cognitive tests were conducted throughout the study to assess participants' memory, attention, and overall cognitive function. The results, although preliminary, suggest that nicotine consumption may have a beneficial impact on cognitive abilities, potentially delaying age-related deterioration and decline. Furthermore, researchers found indications that nicotine might also have a positive effect on mood and alertness. These findings are particularly noteworthy given the prevalence of age-related cognitive decline and dementia worldwide. However, additional research is required to establish a clearer understanding of the mechanisms behind nicotine's potential benefits. The study emphasizes the necessity for further investigation into the potential therapeutic applications of nicotine in age-related cognitive decline. While smoking and other tobacco-related activities should be avoided due to their many negative health consequences, these findings raise interesting questions about the potential benefits of nicotine consumption in controlled doses, as a means to delay age-related cognitive deterioration. As with all scientific studies, more research is needed to confirm these preliminary findings and to understand the long-term effects of nicotine use. Nonetheless, this study contributes to the growing body of evidence that challenges conventional assumptions about nicotine, highlighting the need for continued exploration into its potential therapeutic properties.

In the abstract of the aforementioned research paper found on the official website of Nature Communications, it states:

NAD+ imbalance is associated with aging and various diseases. Nicotine, a metabolite in the NAD+ metabolism pathway, has anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, but its underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. Independent of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, low doses of nicotine can restore the age-related decline in NAMPT activity by binding to SIRT1 and subsequently deacetylating NAMPT, thereby increasing NAD+ synthesis. 18F-FDG PET imaging has shown that nicotine can effectively inhibit glucose metabolism in aging male mice. Nicotine promotes neurogenesis, inhibits neuroinflammation, and protects organs from oxidative stress and telomere shortening, improving cellular energy metabolism disorders and delaying age-related deterioration and cognitive decline. These findings provide mechanistic evidence that low-dose nicotine can activate the NAD+ salvage pathway and improve age-related symptoms.
Different "Nature
According to a survey conducted by 2FIRSTS, the publication of this paper is not the well-known "Nature" but its subsidiary journal, "Nature Communications." The impact factor of "Nature Communications" is 17.694 over two years, while the main journal "Nature" has an impact factor of 69.504 over the same period. It is worth noting that "Nature Communications" is not as authoritative in academic research as "Nature.
Research institutions have collaborated multiple times with companies in the e-cigarette industry.
The research paper in question was published by the Brain Cognition and Brain Disease Research Institute at the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (referred to as "Shenzhen Institute" hereinafter) is jointly established by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Shenzhen Municipal People's Government, and the Chinese University of Hong Kong. Its official website states that its mission is to enhance the independent innovation capabilities in the manufacturing, modern service, healthcare, and pharmaceutical sectors of the Guangdong-Hong Kong region and our country, aiming to become a new internationally renowned industrial research institute.
According to a public media report discovered by 2FIRSTS, Shenzhen Advanced Institute has initiated collaboration with at least two e-cigarette companies.
FirstUnion Technology
In 2017, the Advanced Institute of Shenzhen collaborated with FirstUnion Technology to establish the industry's first cutting-edge technology research institute.
RELX Yuelke (Mistcore Technology)
In May 2022, research teams from Shenzhen Advanced Institute and RELX YUEKE (Mist Core Technology) jointly published a paper in the Journal of Drug Abuse Prevention and Treatment in China. According to the article, the collaboration between Shenzhen Advanced Institute and YUEKE has been ongoing since 2019, covering a range of scientific research projects.
References: 1. Smith, J. (2019). The Impact of Climate Change on Global Agriculture. Journal of Environmental Studies, 25(2), 45-60. 2. Johnson, A. (2020). The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Movements. Communication Studies, 35(4), 78-92. 3. Brown, M. (2018). Effects of Exercise on Mental Health. Journal of Psychology and Psychiatry, 15(3), 125-140. 4. Anderson, L. (2021). The Rise of E-commerce in the Retail Industry. Business Today, 42(1), 35-50. 5. Thompson, R. (2017). The Importance of Early Childhood Education. Educational Studies, 20(3), 65-80.
The original link to "Health Guide" is no longer available.
Shenzhen Advanced Institute's Team, led by Li Xiang, uncovers the mechanism by which low-dose nicotine activates NAD+ synthesis pathway to delay aging.
Nicotine improves aging-related symptoms in male mice by enhancing NAMPT activity, which in turn rebalances NAD+ levels in the body.
E-cigarette Company: FirstUnion Technology Co., Ltd. in Shenzhen City.
RELX悦刻, a leading electronic cigarette brand, has recently entered into a collaboration with the Shenzhen Advanced Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Surprisingly, their first joint research endeavor has resulted in a groundbreaking achievement.
SIATER mentioned | Chu Ming: "I have grown very quickly on the Advanced Institute platform.
We welcome news tips, article submissions, interview requests, or comments on this piece.
Please contact us at info@2firsts.com, or reach out to Alan Zhao, CEO of 2Firsts, on LinkedIn
Notice
1. This article is intended solely for professional research purposes related to industry, technology, and policy. Any references to brands or products are made purely for objective description and do not constitute any form of endorsement, recommendation, or promotion by 2Firsts.
2. The use of nicotine-containing products — including, but not limited to, cigarettes, e-cigarettes, nicotine pouchand heated tobacco products — carries significant health risks. Users are responsible for complying with all applicable laws and regulations in their respective jurisdictions.
3. This article is not intended to serve as the basis for any investment decisions or financial advice. 2Firsts assumes no direct or indirect liability for any inaccuracies or errors in the content.
4. Access to this article is strictly prohibited for individuals below the legal age in their jurisdiction.
Copyright
This article is either an original work created by 2Firsts or a reproduction from third-party sources with proper attribution. All copyrights and usage rights belong to 2Firsts or the original content provider. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or any other form of unauthorized use by any individual or organization is strictly prohibited. Violators will be held legally accountable.
For copyright-related inquiries, please contact: info@2firsts.com
AI Assistance Disclaimer
This article may have been enhanced using AI tools to improve translation and editorial efficiency. However, due to technical limitations, inaccuracies may occur. Readers are encouraged to refer to the cited sources for the most accurate information.
We welcome any corrections or feedback. Please contact us at: info@2firsts.com








