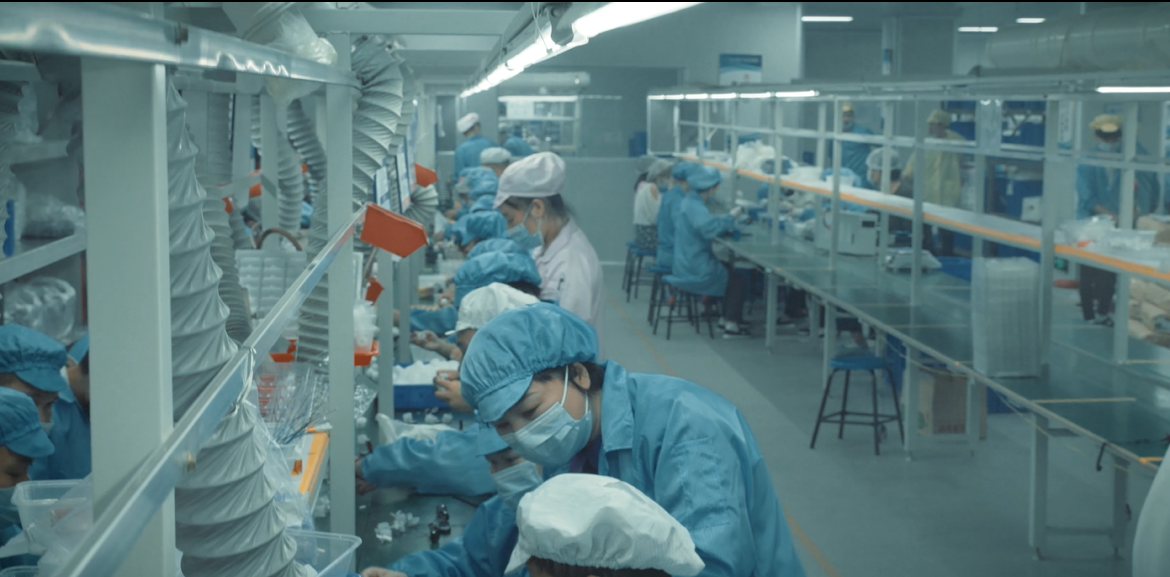
【2Firsts reports from Shenzhen】On November 15, GEEKVAPE unveiled a company video on its WeChat channel, "GEEKVP", showcasing its new manufacturing facility in Indonesia. Opened in 2023, the plant has created more than 1,000 local jobs.

Chinese Vape Companies Continue Expanding in Southeast Asia
In 2022, the trend of Chinese vape companies expanding into Southeast Asia gained momentum, driven by two key factors: the need to reduce U.S. tariff costs and the challenge of obtaining vape operating licenses within China.
2Firsts has previously reported on the shift, noting the relocation of Chinese manufacturers to Indonesia. In July 2022, Smoore, one of the world's largest vape manufacturers, opened its 14th global factory in Malang, Indonesia. The facility spans 6 hectares and is equipped with 16 production lines, each capable of producing 7,200 vape pods per hour.
In August 2022, JIN JIA GROUP (002191.SZ) announced plans to establish a production base in Indonesia, expanding its integrated vape services in the region. Similarly, vape component supplier Huizhou Zhijing Precision confirmed that its Indonesian factory began operations in 2022.
The shift is not limited to Chinese companies. In January 2023, Philip Morris International (PMI) opened a $180 million factory in Indonesia to manufacture IQOS HEETS tobacco sticks. Just months later, in September 2023, South Korea's KT&G revealed plans to build a new factory in East Java, with production set to begin in 2026.
From Spillover to Relocation: The Shifting Challenges of China's E-Cigarette Supply Chain
In 2022, 2Firsts forecasted that while Shenzhen's role as the global hub for vape manufacturing remained secure in the short term, the landscape could evolve.
As major vape companies expand their operations abroad, China's dominant position in the global supply chain is facing new challenges. These companies, with their significant production capacity, exert considerable influence, and their offshore expansions are beginning to ripple through the entire supply chain, akin to the "Apple supply chain migration".
Should key components like atomizers and e-liquids follow suit, overseas factories could evolve into regional manufacturing hubs, diminishing Shenzhen's central role.
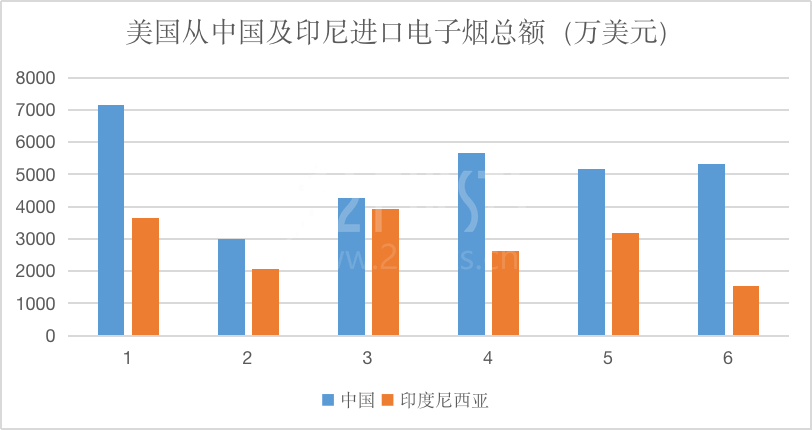
U.S. International Trade Commission data for the first half of 2023 shows that while imports of vapes from China accounted for 63.7% of the market, imports from Indonesia have surged to more than 35%, positioning Indonesia as the second-largest vape exporter after China.
A similar trend is emerging in the nicotine pouch sector. As the global nicotine pouch market surged in 2023, some Chinese manufacturers are no longer considering Shenzhen as a destination for new factories, instead opting for Southeast Asia, such as Malaysia, as a key production hub.
Despite China's dominant position in the global vape supply chain, supported by a strong industrial foundation, the shift of manufacturing to Southeast Asia and other regions is gaining momentum. This trend, while unlikely to disrupt China's central role in the short term, is reshaping global economic dynamics and creating new challenges for vape regulation.
Under the traditional "Shenzhen manufacturing, global consumption" model, China controls the supply chain, while individual countries regulate the market. But if the shift to a "China-led, multi-site manufacturing" model expands, supply chain regulation will become more complex, with new rules emerging across multiple regions.
2Firsts will continue to report the developments in the global vape supply chain.
Readers who wish to share the related imformation or opinions can submit to: info@2firsts.com. The best submissions will be featured on 2firsts.com.
Cover Image:Vaping Production Workshop | Source: "Vaping Twenty Years" Documentary







