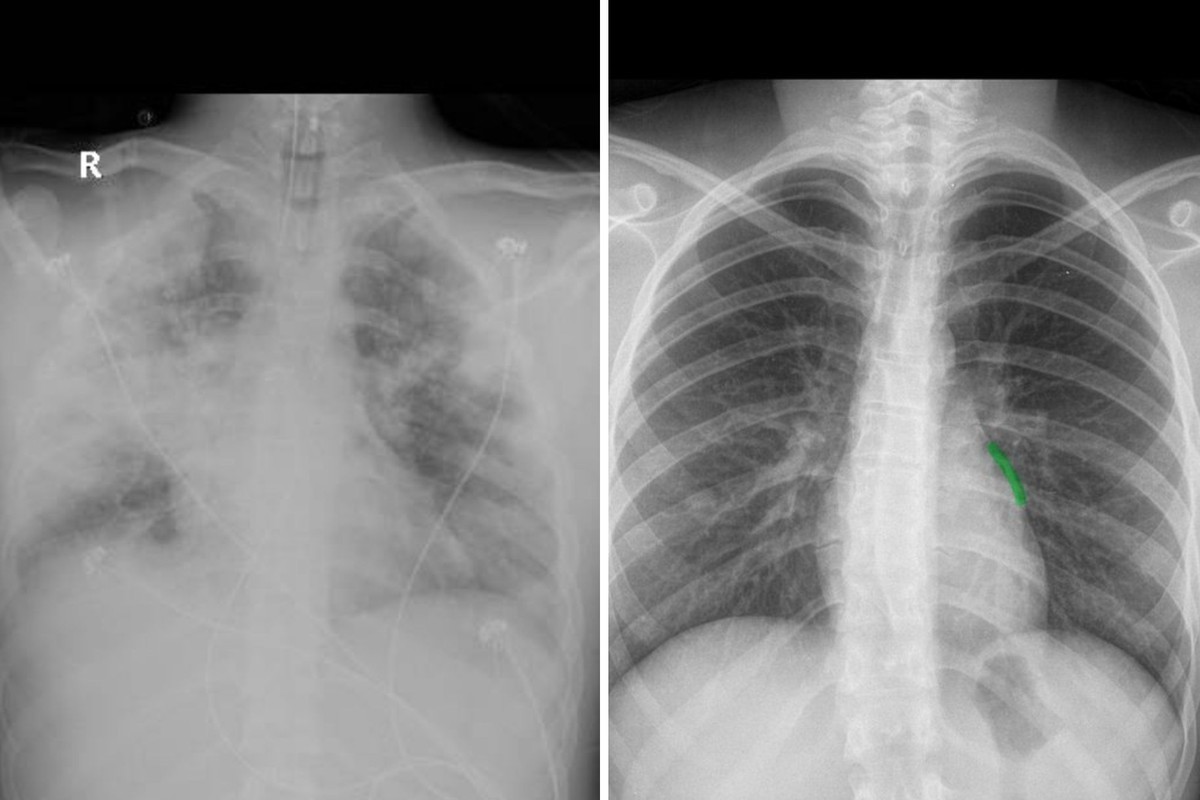
According to a report by Globo on October 16th, a mother named Lya Peva publicly shared the lung X-ray of her deceased son, revealing the potential health risks of e-cigarettes. Lya disclosed that her son started using e-cigarettes at the age of 15, and his lung X-ray showed significant white inflammation. While e-cigarettes were not the direct cause of her son's death at the age of 20, the damage they inflicted on his lungs severely impacted his ability to fight infections.
Dr. Fred Fernandes, a member of the Sao Paulo Respiratory Medicine Association of the Brazilian Society of Internal Medicine, analyzes that lung injuries shown on X-rays may be related to the use of e-cigarettes, known as EVALI, which is a severe inflammatory reaction that can lead to restricted gas exchange.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) first described EVALI in 2019, when numerous young patients were hospitalized with symptoms such as difficulty breathing. Research showed that these patients commonly used e-cigarettes, particularly products containing vitamin E acetate. Although the use of this ingredient has decreased, other substances may still cause long-term lung damage.
A study conducted by the São Paulo State Health Department in conjunction with the Heart Institute and Toxicology Laboratory at São Paulo University Medical School has indicated that e-cigarette users may be six times more likely to experience nicotine poisoning than traditional cigarette smokers. The research also highlighted the inadequate awareness among young people of the addictive risks associated with e-cigarettes, which contain higher levels of nicotine than traditional cigarettes, with some e-cigarettes containing up to 50mg, equivalent to approximately 50 cigarettes.
With the popularity of e-cigarettes, some people are attempting to quit traditional cigarettes by using e-cigarettes, but instead develop a habit of dual usage. This dual usage increases the burden on the heart and lungs, ultimately increasing health risks. It is important for society to take this issue seriously and implement measures to reduce the potential impact of e-cigarettes on public health.
We welcome news tips, article submissions, interview requests, or comments on this piece.
Please contact us at info@2firsts.com, or reach out to Alan Zhao, CEO of 2Firsts, on LinkedIn
Notice
1. This article is intended solely for professional research purposes related to industry, technology, and policy. Any references to brands or products are made purely for objective description and do not constitute any form of endorsement, recommendation, or promotion by 2Firsts.
2. The use of nicotine-containing products — including, but not limited to, cigarettes, e-cigarettes, nicotine pouchand heated tobacco products — carries significant health risks. Users are responsible for complying with all applicable laws and regulations in their respective jurisdictions.
3. This article is not intended to serve as the basis for any investment decisions or financial advice. 2Firsts assumes no direct or indirect liability for any inaccuracies or errors in the content.
4. Access to this article is strictly prohibited for individuals below the legal age in their jurisdiction.
Copyright
This article is either an original work created by 2Firsts or a reproduction from third-party sources with proper attribution. All copyrights and usage rights belong to 2Firsts or the original content provider. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or any other form of unauthorized use by any individual or organization is strictly prohibited. Violators will be held legally accountable.
For copyright-related inquiries, please contact: info@2firsts.com
AI Assistance Disclaimer
This article may have been enhanced using AI tools to improve translation and editorial efficiency. However, due to technical limitations, inaccuracies may occur. Readers are encouraged to refer to the cited sources for the most accurate information.
We welcome any corrections or feedback. Please contact us at: info@2firsts.com








